Photon
is an elementary particle of invariant mass of zero value that
containing certain amount of energy like packets called quantum
energy. Quantum mechanics is a part of physics that developed from
the study of electromagnetic waves in which the quantum of energy is
refers to a specific amount of energy that can be carried by photon
of EM wave at a specific frequency or wavelength. In quantum
mechanics, each photon has a characteristic quantum of energy that
depends on frequency of the EM wave.
| Photons in a Light Wave |
EM
waves are typically described by any one of the following three
physical properties: Frequency, Wavelength and Photon Energy. Photo
energy is the energy carried by a single photon which can be
illustrated by a formula.

The
amount of energy is directly proportional to the photon's
electromagnetic frequency and is inversely proportional to the
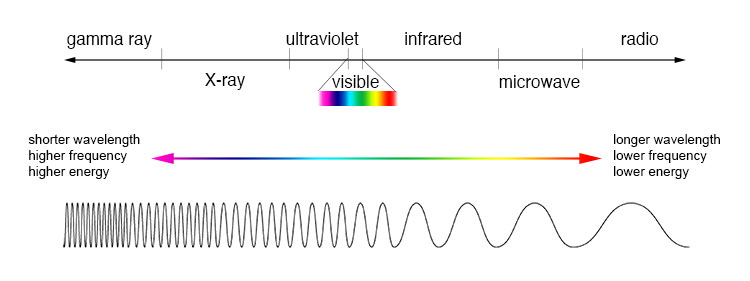
wavelength. In the EM spectrum, the limit for long wavelength is the
size of the Universe itself, while the short wavelength limit is
likely to be the Planck's length. Each photon carries a certain
amount or quantum of energy depending on its wavelength. The shorter
the wavelength of a photon, the greater its frequency and energy.
For example; the lower frequency waves such as infrared, microwave and radiowave has longer wavelengths than the visible light but has lower energy than that of the visible light. The higher frequency waves of shorter wavelengths such as ultraviolet rays, X-rays and Gamma waves has more energy than the visible light which can be harmful to our body. In brief, if our body exposed to infrared rays, our body feels heat and get swept whereas ultraviolet rays cause sunburn.
Comments
Post a Comment